
Abstracts of the 22
nd
National Congress of Digestive Diseases / Digestive and Liver Disease 48S2 (2016) e67–e231
e81
Conclusions:
In this study NUNA Nutritional Navigator as an adjunct
to lifestyle advices, was associated with improved Sofi-MDS and
reduced body weight.
OC.03.4
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF OBETICHOLIC ACID IN PATIENTS
WITH PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS: AN ANALYSIS OF THE
ITALIAN PATIENTS FROM A PHASE 3, RANDOMIZED, PLACEBO-
CONTROLLED STUDY
Andreone P.
1
, Mazzella G.
1
, Invernizzi P.
2
, Floreani A.
3
, Picaro L.A.*
4
,
Adorini L.
5
1
University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy,
2
Humanitas Clinical and
Research Center, Rozzano (MI), Italy,
3
University of Padua, Padua, Italy,
4
Intercept Pharmaceuticals LTD Europe, London, United Kingdom,
5
Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc, S. Diego, California, United States
Background and aim:
Obeticholic acid (OCA) is a potent, selective
farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist currently under investigation for
the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). This study evaluated
the efficacy and safety of OCA for the treatment of PBC.
Material and methods:
This is a subgroup analysis of Italian
patients who participated in an international Phase 3, 12 month,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eligible patients with PBC
who had an alkaline phosphatase (ALP) > 1.67X ULN and/or bilirubin
> ULN but <2X ULN were randomized to receive OCA 5 mg with the
ability to up-titrate to 10 mg after 6 months (Titration OCA), OCA 10
mg or placebo. Patients were permitted to remain on stable doses
ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA). The primary composite endpoint
was the proportion of patients with an ALP <1.67X ULN and a >15%
reduction in ALP and a total bilirubin <ULN.
Results:
Thirty-two out of 216 intent-to-treat patients were at
Italian sites. In the Italian patient group the mean age was 52.3
years, 84% were female, and 94% were on a UDCA. The majority of
patients (91%) completed the double-blind portion of the study. The
percentage of patients at the Italian sites achieving the primary
composite endpoint at 52 weeks was consistent with the total study
population. The baseline values for the placebo, Titration OCA and
OCA 10 mg for: ALP (U/L): 314.6, 302.2, 312.6, respectively; total
bilirubin (µmol/L): 14.4, 12.0, 13.4, respectively; AST (U/L): 56.7,
49.8, 46.5, respectively; ALT (U/L): 60.5, 58.0, 45.4, respectively; GGT
(U/L): 325.4, 287.9, 223.6, respectively. The 12 month values for the
placebo, Titration OCA and OCA 10 mg for: ALP (U/L): 365.9, 188.2,
188.3, respectively; total bilirubin (µmol/L): 16.8, 11.4, 10.8,
respectively; AST (U/L): 62.2, 35.0, 35.7, respectively; ALT (U/L): 61.1,
29.7, 28.8, respectively; GGT (U/L): 298.1, 84.1, and 57.7, respectively.
The laboratory results for the Italian patients were consistent with
the overall population. Mild to moderate pruritus was the most
common treatment emergent adverse event (TEAE) and occurred in
45%, 64% and 50% of patients in the placebo, Titration OCA, 10 mg
OCA groups respectively. There were no differences between the
groups for any other TEAE.
Conclusions:
In this study, OCA (± UDCA) given to patients with PBC
at the Italian sites produced clinically meaningful improvements
in liver biochemistry. The results were consistent with the overall
study population.
OC.03.5
COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT PREDICTS THE OCCURRENCE
OF HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY AFTER TRANSJUGULAR
INTRAHEPATIC PORTOSYSTEMIC SHUNT
Nardelli S.*, Gioia S., Pasquale C., Pentassuglio I., Merli M., Riggio O.
Policlinico Umberto I, Rome, Italy
Background and aim:
Hepatic encephalopathy is a major problem
in patients treated with TIPS. The aim of the study was to establish
whether pre-TIPS covert HE is an independent risk factors for the
development of HE after TIPS.
Material and methods:
82 consecutive cirrhotic patients submitted
to TIPS were included (Gendere 57 M; Age 57.9 ± 10.1 yrs; MELD
11.2 ± 3.6; CPT class A 17, B 53, C 12; TIPS indication: 37 bleeding,
45 refractory ascites). All patients underwent the PHES to identify
those affected by covert HE before TIPS. The incidence of the first
episode of HE taking into account the competing risk nature of the
data (death or liver transplantation) was estimated.
Results:
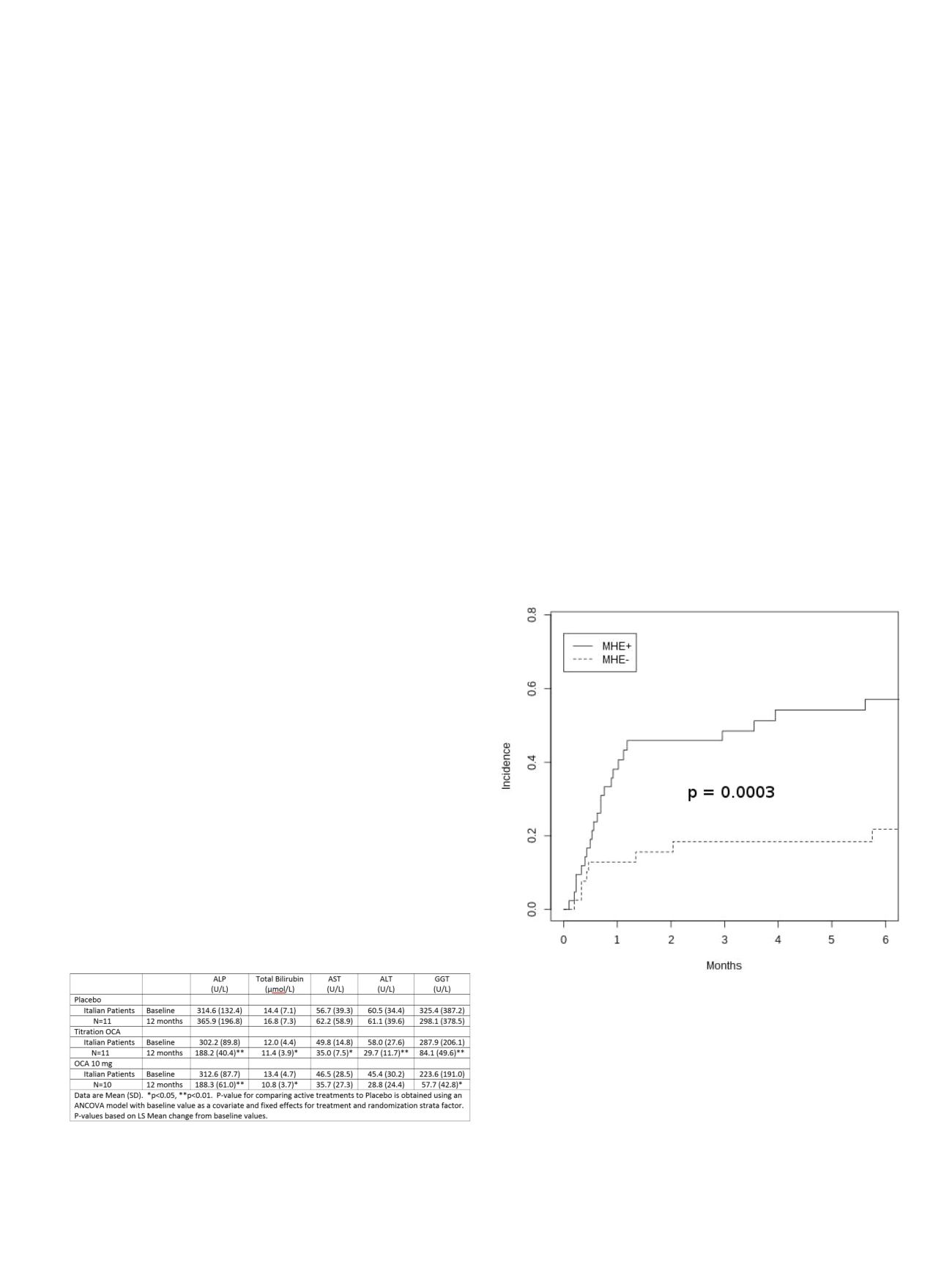
Thirty-five (43%) patients developed overt HE. The
difference of post TIPS HE was highly significant (p=0.0003) between
the patients with or without covert HE before TIPS. Seventy-seven %
of the patients with post TIPS HE were classified as affected by
covert HE before TIPS. Age: (sHR 1.05, CI 1.02-1.08, p=0.002);
C-PSCORE: (sHR 1.29, CI 1.06-1.56, p=0.01) and covert HE: (sHR 3.16
CI: 1.43-6.99 p=0.004) were associated to post TIPS HE. Taking into
consideration only the results of PHES evaluation, the negative
predicting value was 0.80 for all patients and 0.88 for the patients
submitted to TIPS because of refractory ascites. Thus, a patient with
refractory ascites, without covert HE before TIPS, has almost 90%
probability to be free of HE after TIPS.
Conclusions:
Psychometric evaluation before TIPS is able to identify
the large majority of the patients who will develop HE after TIPS
and can be used to select the patients in order to have the lowest
incidence of this important complication.


















