
Abstracts of the 22
nd
National Congress of Digestive Diseases / Digestive and Liver Disease 48S2 (2016) e67–e231
e91
OC.06 Miscellanea 1
OC.06.1
ANALYSIS OF THE EFFICACY OF OCA IN PRIMARY BILIARY
CIRRHOSIS BY VARYING PATIENT DISEASE SEVERITY ACROSS
THREE RANDOMIZED DOUBLE-BLIND, PLACEBO-CONTROLLED
CLINICAL TRIALS
Lutz K.
1
, Pencek R.
1
, Marmon T.
1
, Macconell L.
1
, Picaro L.A.
2
,
Adorini L.*
1
, Shapiro D.
1
1
Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc, S. Diego, California, United States,
2
Intercept Pharmaceuticals LTD Europe, London, United Kingdom
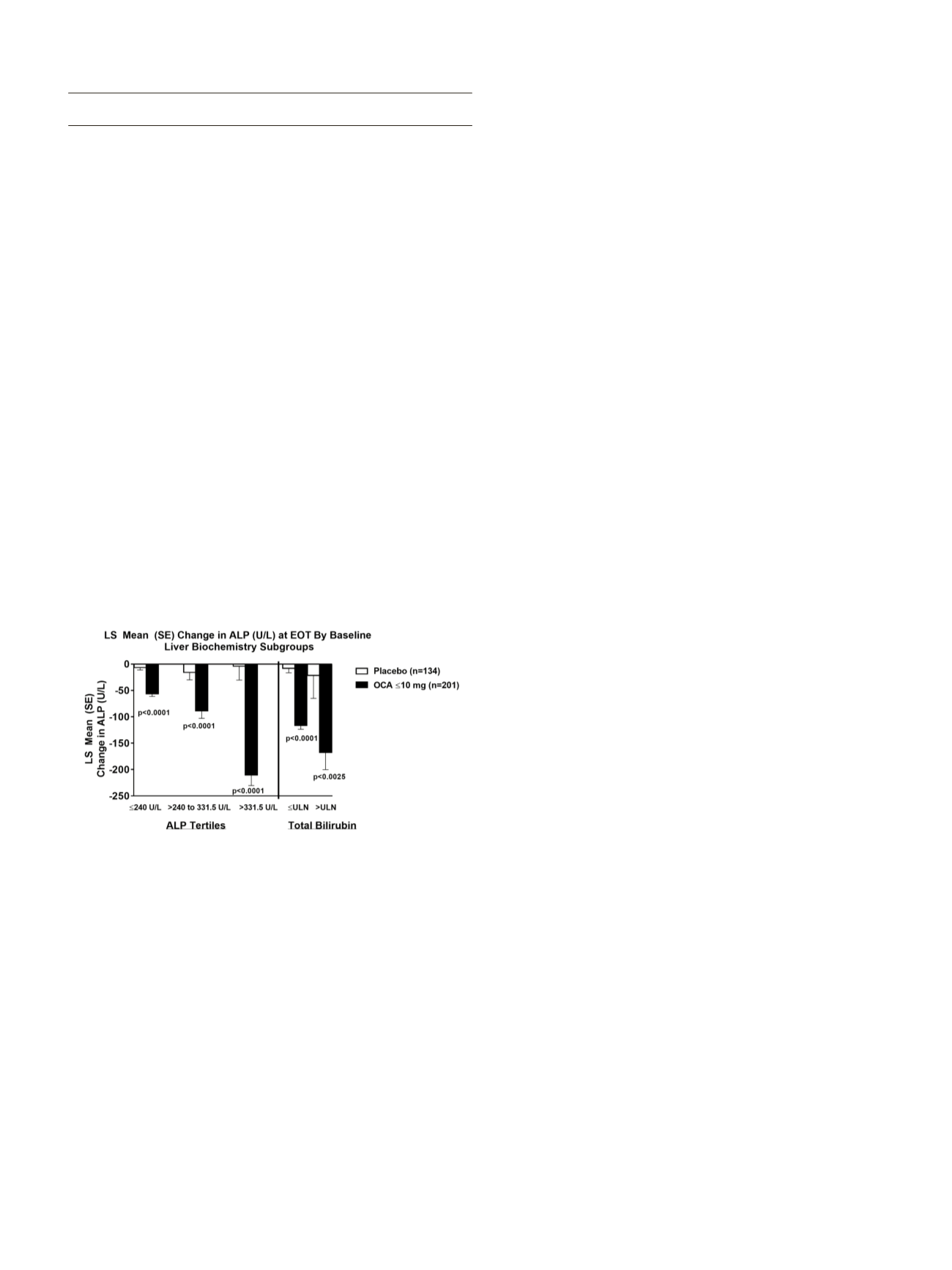
Background and aim:
Obeticholic acid (OCA), a selective and
potent farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist, produced significant liver
biochemistry improvements, including alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
and total bilirubin (bili) in 3 randomized, double-blind (DB) placebo
(PBO)-controlled trials in primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). This
pooled analysis from the 3 trials evaluates efficacy of OCA across a
range of disease severity based on baseline (BL) ALP tertile and total
bili. (≤ULN/>ULN).
Material and methods:
Key inclusion criteria: ALP 1.5 to 10x ULN
and conjugated bili ≤2x ULN for the two 3 month trials and ALP
≥1.67x ULN or total bili >ULN but <2x ULN for the 12 month trial.
Data were pooled based on end of DB treatment (EOT). Treatment
arms were PBO (n=134) and ≤OCA 10 mg (n=201). Endpoints were LS
mean (SE) change from BL to EOT for ALP and percent of patients
achieving a composite endpoint (ALP <1.67 ULN, total bili ≤ULN and
ALP decrease ≥15%), shown to be correlated with long-term survival
in PBC. Safety and tolerability by disease severity were also assessed.
ANCOVA model for p-value (PBO vs active OCA)
Results:
Significant differences for OCA compared with PBO for
both efficacy endpoints were achieved irrespective of PBC disease
severity. The magnitude of ALP reduction was proportional to ALP
tertile suggesting improved response even inmore advanced patients
(Figure). The percentage of OCA patients achieving the composite
endpoint was inversely proportional to BL tertile (68% low, 54% mid,
and 19% upper) and total bili (49%≤ULN, 17%>ULN). Similar results
were observed when subgroups were analyzed by OCA monotherapy
or OCA plus UDCA. Pruritus was the most common adverse event.
The incidence of pruritus for OCA ≤10 mg was similar for the low and
mid tertiles and slightly higher in patients with more severe disease.
Conclusions:
These data demonstrate efficacy of OCA across a range
of PBC severity and confirm ALP and total bili both as continuous
and categorical variables predictive of clinical outcomes.
This integrated analysis demonstrates robust response with OCA
irrespective of BL ALP or total bili. Across the ranges of disease
severity, OCA was safe and well-tolerated. These data are clinically
relevant given that PBC is a chronic and progressive disease, and
demonstrate that even in patients with more advanced disease, OCA
improves parameters shown to correlate with improved clinical
outcomes and reduced risk.
OC.06.2
PANCREATIC CANCER IN WOMEN: LATE ONSET OF MENOPAUSE,
USE OF HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY AND TWO-PARITY
ARE PROTECTIVE FACTORS
Archibugi L.*
1
, Piciucchi M.
2
, Valente R.
1
, Zerboni G.
1
, Stigliano S.
1
,
Signoretti M.
1
, Delle Fave G.
1
, Capurso G.
1
1
Azienda Ospedaliera Sant’Andrea, Roma, Italy,
2
Ospedale Città di
Castello, Città Di Castello, Italy
Background and aim:
The incidence of Pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is slightly higher in men than in women,
although the difference in smoking and alcohol consumption
between the two genders does not explain this disparity completely.
Reproductive and hormonal factors might have an influence, but the
few published data are inconsistent.
The aim of this study is to investigate the role of reproductive and
hormonal factors on PDAC occurrence in women.
Material and methods:
We conducted a unicenter case-control
study on women; risk factors were screened through questionnaires
about gynecologic and medical history. Cases were matched to
controls for age with a 1:2 ratio.
Results:
160 PDAC and 320 matched controls (mean age 70 in both
groups) were enrolled. Age of onset of menopause was significantly
lower in cases (48.9 vs. 50; p=0.02). At a logistic regression
multivariate analysis adjusted for smoking, older age at menopause
(OR:0.9 per year; 95% CI:0.92-1), use of hormonal replacement
therapy (HRT) (OR:0.14; 95% CI:0.04-0.49) and having given birth
to two children (OR:0.62; 95% CI:0.39-0.98) were significant,
independent protective factors. No difference among cases and
controls was found on age of onset of menarche, nulliparity or parity
different from two, use of birth control pill or number of abortions.
Conclusions:
The results of this study provide support for the
hypothesis that PDAC is related to reproductive or hormonal factors.
In our cohort of patients, late onset of menopause, use of HRT and
having given birth to two children are protective factors for the
occurrence of PDAC.
Conversely, age at menarche, history of abortions, multiple abortions,
use of OC, years of use of HRT or OC were not related to risk.
These data confirm some previous findings on menopause age and
number of births while, to our knowledge, this is the first study to
show a protective effect of Hormonal Replacement Therapy.
OC.06.3
PROTECTIVE ACTIVITY OF LACTOBACILLUS RHAMNOSUS GG-
DERIVED FACTORS ON PATHOGEN LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE (LPS)-
INDUCED DAMAGE OF HUMAN COLONIC SMOOTH MUSCLE CELLS
Cicenia A.*
1
, Santangelo F.
1
, Gambardella L.
2
, Iebba V.
1
, Scirocco A.
1
,
Marignani M.
3
, Chirletti P.
1
, Pallotta L.
1
, Carabotti M.
1
, Corazziari E.
1
,
Schippa S.
1
, Severi C.
1
1
University “Sapienza”, Roma, Italy,
2
Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome,
Italy,
3
Azienda Ospedaliera Sant’Andrea, Roma, Italy
Background and aim:
Some of the beneficial effects of probiotics
result to be determined by secreted probiotic-derived factors,
identified as “postbiotic” mediators. The identification of these
soluble factors may represent an opportunity not only to understand
their fine mechanisms of action but also to develop new therapeutic
strategies, that would avoid risks associated with the administration
of live bacteria. Aim of this study was to evaluate if supernatants
harvested from LGG cultures protect human smooth muscle cells
(SMC) from persistent LPS-induced myogenic damage.


















