
Abstracts of the 22
nd
National Congress of Digestive Diseases / Digestive and Liver Disease 48S2 (2016) e67–e231
e99
OC.08 Endoscopy 2
OC.08.1
HIGH-DEFINITION COLONOSCOPY USING I-SCAN IN
MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION AND REAL-TIME
HISTOLOGICAL PREDICTION OF COLONIC NEOPLASTIC
SUPERFICIAL LESION. A SINGLE ITALIAN CENTER PILOT STUDY,
PRELIMINARY RESULTS
Staiano T.*, Grassia R., Savarese M.F., Iiritano E., Bianchi G., Buffoli F.
A.O. Istituti Ospitalieri Di Cremona, Cremona, Italy
Background and aim:
Digital chromoendoscopy (DCE) has the
potential for the in vivo optical diagnosis of colonic neoplastic
superficial lesions.The aimof the present studywas to retrospectively
assess diagnostic accuracy of high definition plus (HD+) colonoscopy
with i-Scan functionality (electronic staining) (morphological and
clinicopathological features of polypoid and non polypoid lesions)
in a single Italian endoscopy unit where was performed routinely
Paris and Kudo classification of all colonic superficial lesion, by real-
time image processing during colonoscopy.
Material and methods:
The study population consisted of 1288
consecutive adult patients undergoing colonoscopy. Indications for
the procedure were screening, post polypectomy surveillance,
symptomatic pts. They undergo to HD+ colonoscopy in conjunction
with i-Scan surface enhancement (90i series, Pentax). Detected
colorectal lesions were judged according to type, location, and size.
The assessment of the colon was started when the cecum had been
reached and the surface enhancement function (SE mode) was
activated throughout the withdrawal of the instrument.Histology
was predicted in real time and biopsies or resections were performed
on all identified lesions. Diagnostic efficacies (sensitivity, specificity,
positive predictive values, negative predictive values, diagnostic
accuracy) for the prediction of adenomatous polyps will be
calculated with reference to the histological diagnosis. A total of
1633 colorectal lesions were analyzed:264 hyperplastic (HP), 1080
tubular adenomas (TA), 145 tubulo–villous adenoma (ATV), 6 villous
adenoma (VA), 6 carcinomaswith intramucosal to scanty submucosal
invasion and 13 carcinomas with massive submucosal invasion (SM-
m). Lesions were observed by (HD+) with i-Scan endoscopy and
were classified according to pit appearances: outcome measurement
was the accuracy of the histologic real time prediction of neoplastic
and non neoplastic lesions of DCE.
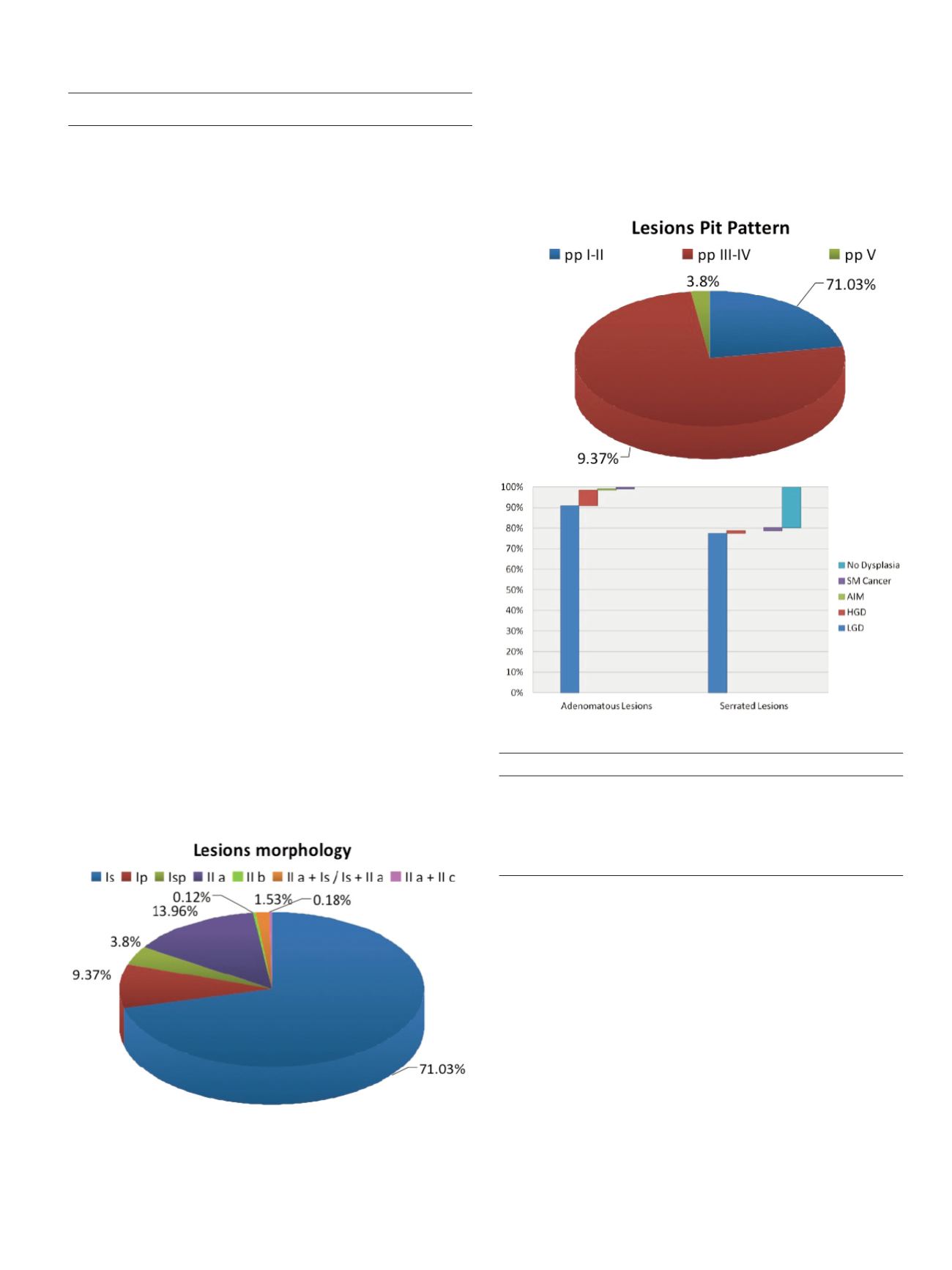
Results:
Histologic findings of HP and A were seen in 16,35% and
80,93% of all lesions. Sensitivity and specificity of pit pattern I/II for
a diagnosis of HYP were 84,9% and 92,2%, accuracy 91%; positive
predictive value: 72,4%; negative predictive value: 96,2% those of pit
pattern III / IV for a diagnosis of TA,TAV,AV were 91,8% and 84,3%
respectively, accuracy 90%; positive predictive value:96%; negative
predictive value: 71,5%; pit pattern Vi/Vn for a diagnosis of ADK
were 70,6% and 99,1% and accuracy of 98%; positive predictive
value:70,6%; negative predictive value:99,1% HD + endoscopy with
I-scan have been confirmed to be highly predictive of deep
submucosal invasion with a 98% overall accuracy.
Table
Diagnostic accuracy of glandular pattern in histological prediction
Sensitivity Specificity VPP VPN Accuracy
Non neoplastic
84.9%
92.2% 72.4% 96.2% 90.8%
pattern (pp I-II)
Neoplastic non
91.8%
84.3% 96% 71.5% 90.3%
invasive pattern (pp III-IV)
Neoplastic invasive
70.6%
99.1% 70.6% 99.1% 98%
pattern (pp Vi-Vn)
Conclusions:
HD+ colonoscopy with i -Scan findings of colorectal
lesions were associated with histologic grade and invasion depth.
These results suggest that in the examination of colonic lesions the
i - scan system provides imaging features additional to conventional
endoscopy.
OC.08.2
A SINGLE CENTER EXPERIENCE OF NOVEL LUMEN-APPOSING
METAL STENT FOR ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND-GUIDED
DRAINAGE
Anderloni A.*, Di Leo M., Carrara S., Loriga A., Repici A.
Humanitas, Rozzano (Mi), Italy
Background and aim:
Recently new specifically designed devices for
interventional EUS such as Hot-AXIOS™ have significantly changed
the technical approach in this setting allowing a simple, safe and


















