
e194
Abstracts of the 22
nd
National Congress of Digestive Diseases / Digestive and Liver Disease 48S2 (2016) e67–e231
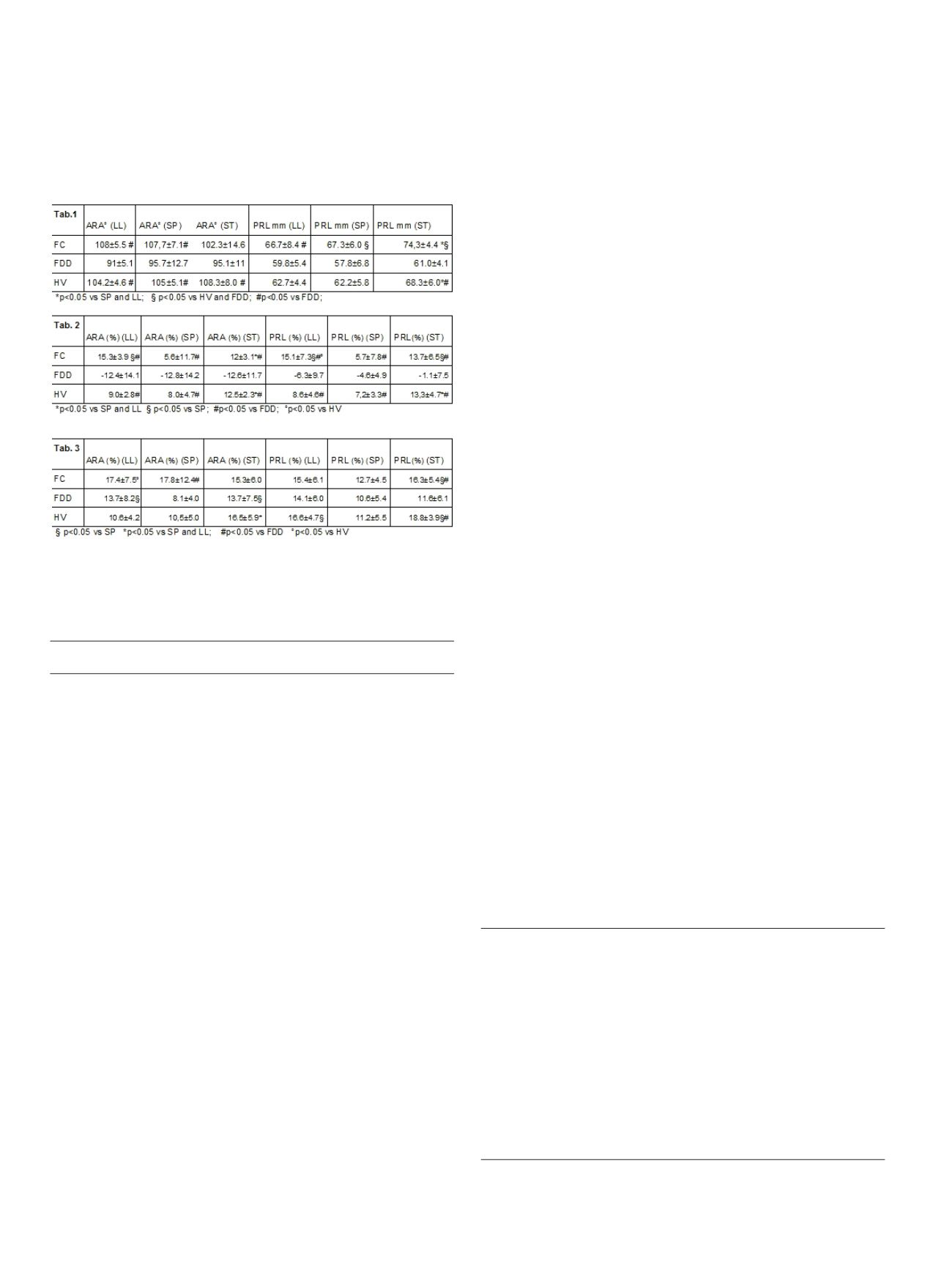
with LL and SP. PRL values were lower in FDD than in HV and FC
because of contraction or lack of relaxation of PR. During push
straining in HV and FC, PR relaxation was better in ST than in SP and
in LL a trend toward a less paradoxical contraction of PR was seen in
FDD. During squeezing in HV and FC, contraction is less effective in
SP than in ST and LL.
Conclusions:
ST is the most effective position to study the pelvic
floor dynamics and FDD.
P.14 IBD 2
P.14.1
EVALUATION OF BONE METABOLISM DURING ANTI-TNF THERAPY
IN INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASES
Petruzzellis C.*, Sparano L., Cesari P., Boselli C., Pagani F.
Ospedale Fondazione Poliambulanza, Brescia, Italy
Background and aim:
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are
associated with increased risk of developing osteopenia or
osteoporosis. This is due to many factors some of which related to
disease activity, such as increased concentration of pro-inflammatory
citokines, and some related to the specific therapies. In particular, in
addition to its role in the pathogenesis of intestinal inflammation,
the TNF-
a
has direct, detrimental effects on osteoblast activity.
Osteoblast are responsible for bone formation, whereas osteoclast
are responsible for bone resorption, the two phases are coupled
in bone remodeling. Aim of the study was to examine short-term
changes in biomarkers of bone formation, serum procollagen type
I N propeptide (PINP), and bone resorption, serum collagen type
I C-telopeptide (CTX), as recommended by IOF/IFCC, following
initiation of anti-TNF-
a
therapy (Infliximab, IFX) and the association
with disease activity over 54 weeks of IFX therapy.
Material and methods:
Serum samples for bone markers were
collected at baseline (T0), before starting the therapy, and every
two months. At T0 patients underwent (1) clinical evaluation, (2)
endoscopic evaluation, (3) inflammatory laboratory test (reactive
protein C (RPC) and fecal calprotectin, and (4) measurement of bone
mineral density using dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA).
Every two months patients underwent through the steps 1) and 3).
All the patients (pts) showed no sign of osteopenia or osteoporosis
at DEXA.
Results:
A preliminary analysis of the first 5 enrolled pts, after two
months of IFX therapy, showed: 2 pts with baseline levels of CTX
within reference interval (RI) and elevated levels of PINP had an
increase of CTX and a decrease of PINP; 3 pts with baseline levels of
both CTX and PINP within RI had unmodified CTX levels but increase
of PINP. Almost all pts showed biochemical inflammation and
endoscopic-clinical moderate activity at T0 and a clinical response
and normalization of RPC at T2.
Conclusions:
Our findings indicate amodulation effect of IFX therapy
on osteoblast in all pts, but a heterogeneous effect on osteoclast
activity. These results represent preliminary but promising data that
could expand knowledge of the interactions between cytokines and
bone in the bone-remodeling process.
P.14.2
IS TOPICAL THERAPY UNDERUSED IN PATIENTS WITH
ULCERATIVE COLITIS? OUR EXPERIENCE
Benazzato L.*
2
, Ferronato A.
1
, Azzurro M.
2
, Accordi C.
2
, Zorzetto V.
2
,
Marchiaro G.
2
, Carone N.
2
, Franceschi M.
1
, Tomba F.
1
, Messina O.
1
,
Baldassarre G.
1
1
UOSVD Endoscopia ULSS 4 Alto Vicentino, Santorso (VI), Italy,
2
U.O.C.
Gastroenterologia, Ospedale Mater Salutis, Legnago (VR), Italy
Background and aim:
Rectal administration of 5-ASA/steroids is
the treatment of choice for ulcerative colitis (UC), particularly for
left-sided/distal forms. Little is known about the adherence rates to
rectal therapies, and some studies demonstrated an adherence as
low as 30% in patients with UC. We aim to quantify the prevalence
of non-adherence to rectal therapies in UC patients recruited for the
first time in 2 dedicated IBD unit in Legnago Hospital (Verone) and
Alto Vicentino Hospital (Santorso, Vicenza).
Material and methods:
We retrospectively collected demographical
and clinical variables of patients admitted for the first time in the
IBD outpatients units from august 2012 to september 2015.
Results:
135ulcerative colitis patientswere recruited. Demographical
and clinical variables are summarized in table 1 and 2. 46 pts (34%)
had pancolitis, 20 (15%) left sided colitis, 45 (33%) procto-sigmoiditis
and 24 (18%) proctitis. Topical therapy with 5-ASA or steroids was
given in 6 (9%) pts with proctitis/proctosigmoiditis, a combined
systemic and topical treatment was given in 28 pts (41%), whereas
systemic treatment with 5-ASA alone was given in 31 (45%) patients.
Proportions of topical drug use decreased with respect to disease
extension from 34 (49%) pts for proctitis/proctosigmoiditis to 12
(26%) pts for pancolitis (p=0,01). There was no association between
disease activity and the use of topical therapy.
Table 1
Patients
Males
71 (53%)
Females
64 (47%)
Age
49.7 (18-89)
Disease duration
8.8 (0.1-53)
Disease extention
Pancolitis/extensive colitis
46 (34%)
Left-sided colitis
20 (15%)
Proctosigmoiditis
45 (33%)
Proctitis
24 (18%)
Disease activity
Remission (Mayo < 2)
61 (45%)
Mild (Mayo 2-4)
56 (42%)
Moderate (Mayo 5-7)
13 (9%)
Severe (Mayo > 7)
5 (4%)


















