
Abstracts of the 22
nd
National Congress of Digestive Diseases / Digestive and Liver Disease 48S2 (2016) e67–e231
e211
or as a secondary option after plastic stent disfunction. Short and
long term efficacy was accertained after one and three months on
the basis of clinical and laboratory findings.
Results:
57 patients were included (M: 28, mean age: 72.3 years). 48
were affected by malignant and 7 by benign biliary stenosis, 2 were
trated for difficult choledoco-lithiasis. In 16 patients, CSEMS were
deployed after dysfunction of plastic stent.
Short term (1 months) efficacy was obtained in 53/55 patients;
other two patients were lost to follow-up. Early (within one
week) complications included: bleeding (3), cholangitis (1), distal
migration (1), pancreatitis (1), retroperitoneal perforation (1).
Late complications were: migration (2), clogging (2), cholecystitis (2).
Clinical success after three months was obtained in 45/50 patients
(3 patients lost to follow-up). Among these patients we observed: 1
stent dysfunction due to clogging after one month, 2 cholecystitis
and 2 distal migrations.
Conclusions:
In our experience biliary FCSEMS appeared safe and
efficient expecially for the treatment of biliary stenosis. We achieved
a high success rate with low early and late complications, both when
used as first line treatment or after plastic stent disfunction.
P.16.15
FAMILIAL ADENOMATOUS POLYPOSIS SMALL BOWEL
SURVEILLANCE: COULD INDICATORS FOR VIDEO-CAPSULE
ENDOSCOPY BE ASCERTAINED?
Papagni S.*, Rizzi S., Principi M., Albano F., Iannone A., Contaldo A.,
Losurdo G., Ierardi E., Di Leo A.
UO Gastroenterologia universitaria, Policlinico di Bari, Bari, Italy
Background and aim:
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is a
genetic disease characterized by multiple colonic adenomas. Small
intestinal polyps (SIPs) may occur in FAP with possible malignant
transformation. However, conventional endoscopy cannot explore
the whole small bowel. Only videocapsule endoscopy (VCE) could
be used for this purpose. Aim of the study was to evaluate, by VCE,
prevalence and possible indicators of SIPs in FAP patients.
Material and methods:
Twelve FAP patients underwent VCE and
upper endoscopy for duodenal polyposis staged by Spigelman score.
Mutational analysis was additionally performed. Fisher’s and t test
were used for statistical analysis.
Results:
Eight patients showed SIPs at VCE (66.6%) as well as
eight patients had duodenal polyposis (1 patient with SIPs did
not demonstrate duodenal polyps). Patients with SIP had higher
Spigelman score than those without. The presence of SIP directly
correlated with the Spigelman score.
Conclusions:
VCE could be proposed as SIPs surveillance in FAP
patients with particular clinical/endoscopic features.
P.17 Endoscopy 3
P.17.1
COMPARISON BETWEEN DIFFERENT BOWEL PREPARATION
REGIMENS FOR COLONOSCOPY: A SINGLE-CENTRE
OBSERVATIONAL STUDY
Messina O.*
1
, Franceschi M.
1
, Tomba F.
1
, Ferronato A.
1
, Sella D.
1
,
Cocco A.
1
, Migliorini S.
1
, Mosele M.
1
, Rosa L.
1
, Salin E.
1
, Vidale M.
1
,
Vanzetto E.
2
, Toffanin R.
2
, Baldassarre G.
1
1
Endoscopic Unit. Department of Surgery, ULSS4 Alto Vicentino,
Santorso (VI), Italy,
2
Department of Public Health, ULSS4 Alto
Vicentino, Santorso (VI), Italy
Background and aim:
Adequate bowel preparation is the key
of a successful colonoscopy. The aim of this study was to analyse
and compare different bowel preparation regimens and clinical
characteristics of patients referred for colonoscopy to our centre.
Material and methods:
We conducted a retrospective study
from January 2014 to September 2015. Data were collected from
colonoscopies reports and included sex, age, body mass index (BMI),
comorbidities, type of bowel preparation, dosage and split vs single
administration. Bowel cleansing was evaluated using the 5-point
Aronchick rating scale for each colonic segment, where overall
quality of A or B were considered a criterion of successful bowel
preparation. Deep sedation was routinely offered to patients.
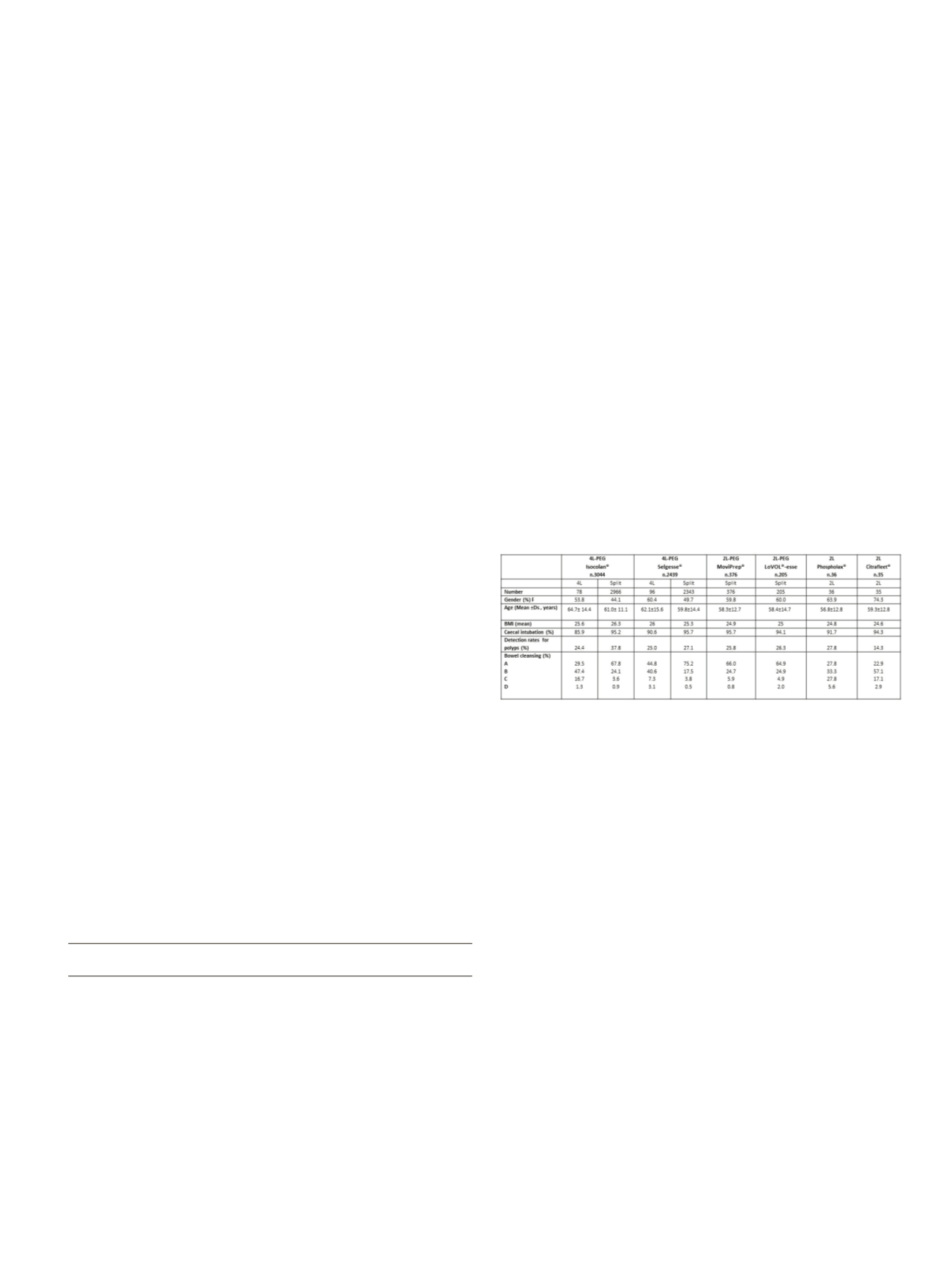
The bowel preparation were: 4L PEG (Isocolan®), 4L PEG +
simethicone (Selgesse®), 2L PEG + Asc (MoviPrep®), 2L PEG
with citrate and simethicone plus bisacodyl (LoVOL®-esse), 2L
Phospholax and 2L Citrafleet.
Results:
Of the 6,720 patients evaluated 6,135 (M=3164, F=2971,
mean age=60.3 ± 12.9 years, range=18-92) were included in the
analysis.
Successful bowel cleansing was achieved in 5189 of 6135 pts (92.0%)
without significant differences for high and low volume (p=0.548).
Split-dose is significantly effective respect to single administration
(p=0.0001).
In 5838 pts (95.2%) was achieved the cecal intubation. Detection
rates for polyps was 32% and for neoplasm was 1.6%.
The table shows the main characteristics of patients divided
according to bowel preparation.
Conclusions:
According to International Guidelines, in our cohort
the split-dose, but not high or low volume, was judged more effective
than one single-dose bowel preparation and was significantly
associated with the indicators of quality.
P.17.2
USEFULNESS OF PROPHYLACTIC HEMOCLIPS PLACEMENT IN
MINIMIZING DELAYED POST-ENDOSCOPIC MUCOSAL RESECTION
BLEEDING IN GASTRIC SUPERFICIAL LESIONS: RETROSPECTIVE
STUDY
Imperatrice B.*, Desideri F., Angeletti S., Ruggeri M., D’Ambra G.,
Corleto V.D., Di Giulio E.
Sant’Andrea Hospital, Rome, Italy
Background and aim:
Bleeding events are one of the potential
severe complications after endoscopic polypectomy, occurring
immediately or delayed. At the present time, there are no existing
data in literature about the prophylactic placement of hemoclips
after gastric endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) in minimizing
delayed post-endoscopic mucosal resection bleeding (pEMRb).
However, with the availability of endoscopic hemoclips their
prophylactic placement is spreading. Our aim was to evaluate the
usefulness of this practice after gastric EMR in reducing the rate of
delayed pEMRb in a retrospective study.
Material and methods:
A retrospective analysis of consecutive
operative gastroscopies with a hot-snare en-bloc EMR at our Unit
between 04/2008-02/2015 was performed. Single-use Olympus
standard clip were applied. Hemoclips prophylactic placement was


















