
Abstracts of the 22
nd
National Congress of Digestive Diseases / Digestive and Liver Disease 48S2 (2016) e67–e231
e153
occurred during colonoscopy in outpatient suffering from ulcerative
colitis (UC), which was successfully treated with endoscopic
clipping.
Material and methods:
In april 2015, we observed an outpatient
42 years old man with UC from 21 years, was sent at our hospital to
undergo a routine surveillance colonoscopy in our Unit of Digestive
Endoscopy. His past family and medical history, and physical
examination were unremarkable. Routine laboratory tests and
complete blood analysis were normal. The patient was in clinical
remission and actually treated with mesalazine 3,2 gr./daily. A total
colonoscopy, with conscious sedation and without the use of CO2
insufflation, at that time not available, was performed after standard
bowel preparation with 4 liters of polyethylene glycol lavage
solution using a split-dose regimen. Colonoscopic findings revealed
a mild erythema with granular mucosa in the rectum, and evidence
of multiple scars in left colonic segment explored.
Results:
During withdrawal of the endoscope, two longitudinal
MT with a length of about 8 and 12 millimiters involving mucosa
and submucosa were revealed in sigmoid colon, whereas such
MT were not observed during the insertion of the endoscope.
Therefore, immediately, ten endoclips Resolution ™ (Boston
Scientific Corporation, Natick, USA) were used for mucosal clousure
of the colon wall, without evidence of active bleeding. The patient
was hospitalized in the department of surgery, and to exclude the
suspicion of a perforation, an abdominal CT scan was performed,
which showed the absence of pneumoperitoneum. The patient’s
postoperative clinical course was uneventful, with a liquid diet and
parenteral antibiotic therapy, and he was discharged three days after
admission.
Conclusions:
MT are rare and uncommon complication during
colonscopy, have not been reported in the colonic mucosa of patients
with UC. Mucosal inflammation alone is not sufficient to explain the
cause of MT. One possible mechanism for MT could be attributed
to the stiffness of the mucosal and submucosal layers, as well as
the presence of multiple scars, possibly in combination with the
pressure of the air resulting from endoscopic insufflation, leading to
stretching of the colon wall mucosa and subsequent tearing.
P.06 Coeliac Disease 1
P.06.1
USEFULNESS OF LASER DOPPLER PERFUSION IMAGING TO
OBJECTIFY THE ORAL MUCOSA PATCH TEST IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF
ALLERGIC CONTACT MUCOSITIS IN NICKEL-SENSITIVE PATIENTS
Borghini R.*
1
, Puzzono M.
1
, Rosato E.
2
, Di Tola M.
1
, Greco F.
1
,
Di Nardi S.
1
, Picarelli A.
1
1
Department of Internal Medicine and Medical Specialties, Sapienza
University, Roma, Italy,
2
Department of Clinical Medicine, Clinical
Immunology Unit-Scleroderma Center, Sapienza University, Roma,
Italy
Background and aim:
Nickel (Ni) is often the trigger of gastro
intestinal and systemic disorders: the exposure of intestinal mucosa
to Ni may cause an Allergic Contact Mucositis (ACM), identifiable by
means of the Ni oral mucosa Patch Test (omPT). The effectiveness of
omPT has already been proven, but up today an objective diagnostic
approach to Ni ACM still lacks.
AIM: Laser Doppler Perfusion Imaging (LDPI) was tested to support
omPT in Ni ACM diagnosis.
Material and methods:
Popultaion: Group A: 22 patients with
intestinal and/or systemic symptoms related to the ingestion of Ni-
containing foods. Group B: 12 asymptomatic volunteers. Ni-related
gastrointestinal and/or extra-intestinal symptoms and their severity
were tested by a specific alimentary-symptom questionnaire. All
patients underwent Ni omPT with clinical evaluation at baseline
(T0), after 30 minutes (T1), after 2 hours (T2) and after 24-48 hours
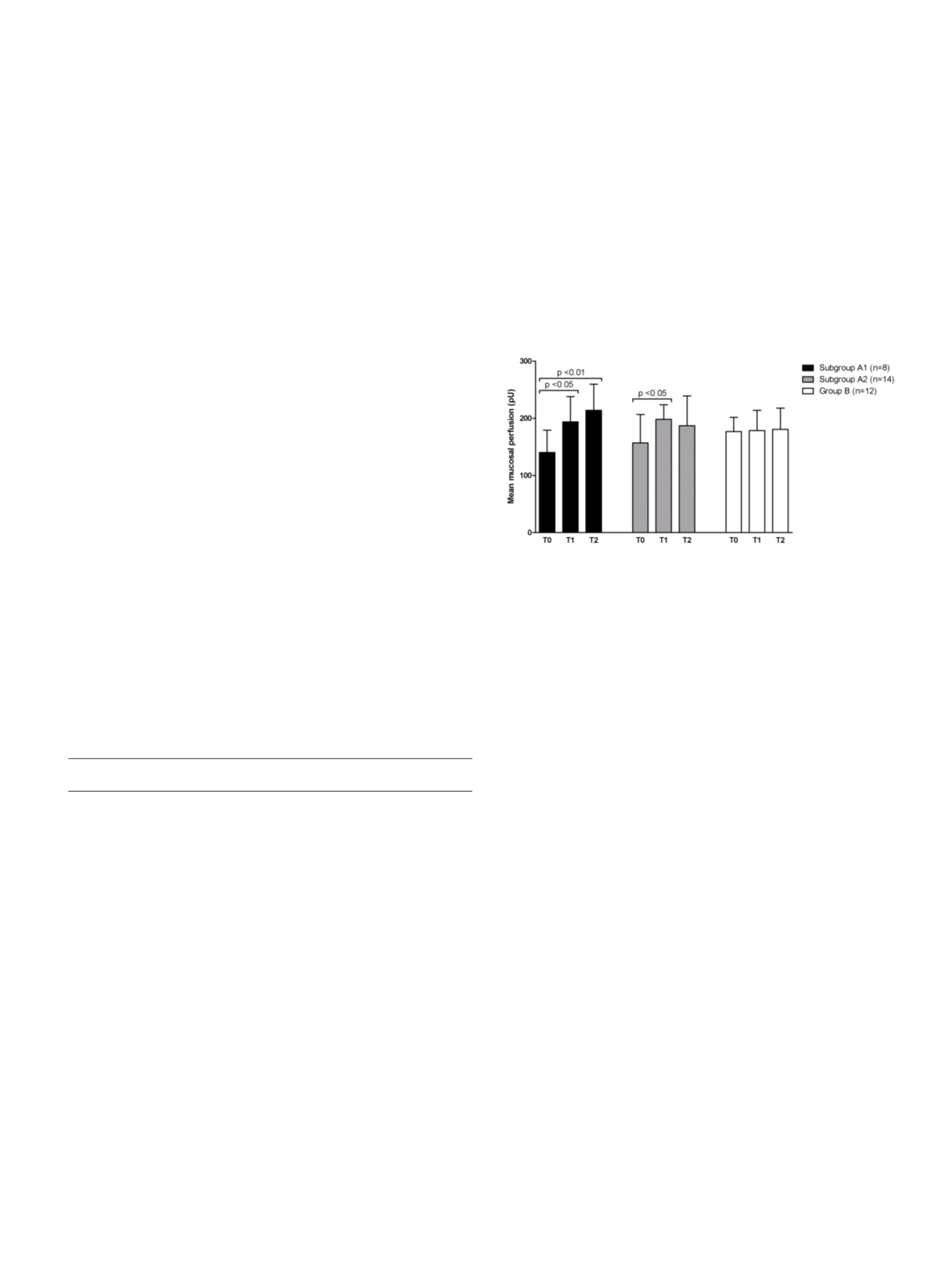
(T3). LDPI was performed to evaluate the mean mucosal perfusion at
T0, T1 and T2. Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA test and
Bonferroni multiple-comparison test.
Results:
All 22 Ni-sensitive patients (group A) presented oral
mucosa hyperemia and/or edema at T2. Eight out of the same 22
patients presented a local delayed vesicular reaction at T3 (group
A1), unlike the remaining 14 out of 22 patients (group A2). All 12
patients belonging to control group B did not show any alteration.
Mean mucosal perfusion calculated with LDPI showed an increase in
both subgroup A1 and A2. In group B, no significant perfusion
variations were observed.
Conclusions:
omPT properly supported by LDPI may actually be
used for diagnostic purposes in ACM to Ni. This also applies to those
symptomatic Ni-sensitive patients who do not have the typical
aphthous stomatitis after 24-48 hours from Ni omPT and could risk
to miss the diagnosis.
P.06.2
HOW MUCH DO CELIAC PATIENTS KNOW ABOUT GLUTEN FREE
DIET?
Bruno M., Marengo A., Bufis M., Sprujevnik T., Astegiano M.*
Ospedale Molinette, Turin, Italy
Background and aim:
The only treatment for Celiac Disease at
present is a strict lifelong gluten-free diet (GFD) which decreases
disease-related mortality and has a role in preventing some of the
long-term complications. Adherence to GFD has been the object
of many studies but few have investigated its essential requisite:
a thorough knowledge of gluten sources. Our aim was to measure
celiac patients’ knowledge of GFD and assess its determinants.
Material and methods:
Between March and December 2014 a 20-
item questionnaire was submitted to our celiac outpatients who
were asked to indicate which foods or situations might be at risk of
gluten intake. Half of the questions involved foods/situations that
really expose patients at risk of consuming gluten while the other
half concerned products that are gluten-free. A 20-point rating scale
was built giving one point for each correct answer.
Results:
154 patients were enrolled. The mean score of the
knowledge test was 14.3 ± 2.9. Focusing on the incorrect responses,
only 20.8% of them would have placed patients at risk of consuming
gluten while the other 79.2% concerned foods or situations that were
unnecessarily avoided by the patients. A statistically significant
lower score was obtained by patients aged over 60 years (p=0.0002),
without a degree or diploma (p=0.0016), non-members of the Italian
Celiac Association (p=0.043), who never logged to the Association
website (p=0.0002) and never ate outside (p=0.0009). Conversely
no significant correlation was observed between gender, kind of


















